Redgate provides Compliant Database DevOps solutions for the finance, healthcare, and technology sectors, plus ingeniously simple tools for SQL Server,.NET, and Oracle. 此下载不包括 JDK。您可以连接并使用任何 JDK 1.8 或更高版本。 安装和运行步骤: - 确保您安装了 JDK,如果未安装,请在这里下载 (对于 64 位 Intel Macs,请下载 Java for Mac OS X 10.5 Update 1。 对于新版本的 Mac OS,请使用'软件更新'特性). RazorSQL - Query, Edit, Browse, and Manage Databases RazorSQL is an SQL query tool, database browser, SQL editor, and database administration tool for Windows, macOS, Mac OS X, Linux, and Solaris. RazorSQL has been tested on over 40 databases, can connect to databases via either JDBC or ODBC, and includes support for the following databases.
- Sql Server Data Tools For Mac Os
- Sql Server Data Tools For Mac
- Sql Server Command Line Tools For Mac
- Sql Server Tools For Mac
- Sql Server Query Tool For Mac
- Sql Server Tool For Mac Installer
- Microsoft Sql Server Tools For Mac
I previously explained how to install SQL Server on a Mac via a Docker container. When I wrote that, SQL Server 2017 was the latest version of SQL Server, and it had just been made available for Linux and Docker (which means that you can also install it on MacOS systems).
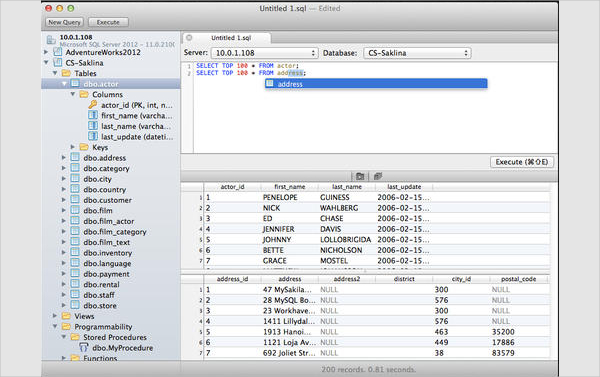
SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) is a modern development tool for building SQL Server relational databases, databases in Azure SQL, Analysis Services (AS) data models, Integration Services (IS) packages, and Reporting Services (RS) reports.
In late 2018, Microsoft announced SQL Server 2019 Preview, and subsequently announced general release in late 2019. The installation process for SQL Server 2019 is exactly the same as for SQL Server 2017. The only difference is that you need to use the container image for SQL Server 2019 instead of the 2017 image. Here I show you how to do that.
Also, if you already have SQL Server 2017 installed, and you want to install SQL Server 2019 without removing the 2017 version, you'll need to allocate a different port number on your host. I show you how to do that too.
Docker
The first step is to install Docker. If you already have Docker installed you can skip this step (and jump straight to SQL Server).

Docker is a platform that enables software to run in its own isolated environment. Therefore, SQL Server 2019 can be run on Docker in its own isolated container.
Install Docker
To download, visit the Docker CE for Mac download page and click Get Docker.
To install, double-click on the .dmg file and then drag the Docker.app icon to your Application folder.
Launch Docker
Launch Docker the same way you'd launch any other application (eg, via the Applications folder, the Launchpad, etc).
When you open Docker, you might be prompted for your password so that Docker can install its networking components and links to the Docker apps. Go ahead and provide your password, as Docker needs this to run.
Increase the Memory (optional)
By default, Docker will have 2GB of memory allocated to it. I'd suggest increasing it to 4GB if you can.
To do this, select Preferences from the little Docker icon in the top menu:
Then finish off by clicking Apply & Restart
SQL Server
Now that Docker has been installed and configured, we can download and install SQL Server 2019.
Download SQL Server 2019
Open a Terminal window and run the following command.
This downloads the latest SQL Server for Linux Docker image to your computer.
You can also check for the various container image options on the Docker website if you wish.
Launch the Docker Image
Run the following command to launch an instance of the Docker image you just downloaded:
Just change
Bartto a name of your choosing, andreallyStrongPwd#123to a password of your choosing.If you get a 'port already allocated' error, see below.
Here's an explanation of the parameters:
-e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y'- The
Yshows that you agree with the EULA (End User Licence Agreement). This is required. -e 'SA_PASSWORD=reallyStrongPwd#123'- Required parameter that sets the
sadatabase password. -p 1433:1433- This maps the local port 1433 to port 1433 on the container. The first value is the TCP port on the host environment. The second value is the TCP port in the container.
--name Bart- Another optional parameter. This parameter allows you to name the container. This can be handy when stopping and starting your container from the Terminal. You might prefer to give it a more descriptive name like
sql_server_2019or similar. -d- This optional parameter launches the Docker container in daemon mode. This means that it runs in the background and doesn't need its own Terminal window open. You can omit this parameter to have the container run in its own Terminal window.
mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2019-latest- This tells Docker which image to use.
Password Strength
You need to use a strong password. Microsoft says this about the password:
The password should follow the SQL Server default password policy, otherwise the container can not setup SQL server and will stop working. By default, the password must be at least 8 characters long and contain characters from three of the following four sets: Uppercase letters, Lowercase letters, Base 10 digits, and Symbols.
Error – 'Port already allocated'?
If you get an error that says something about 'port is already allocated', then perhaps you already have SQL Server installed on another container that uses that port. In this case, you'll need to map to a different port on the host.
Therefore, you could change the above command to something like this:
In this case I simply changed
-p 1433:1433to-p 1400:1433. Everything else remains the same.You may now get an error saying that you need to remove the existing container first. To do that, run the following (but swap
Bartwith the name of your own container):Once removed, you can try running the previous command again.
Note that if you change the port like I've done here, you will probably need to include the port number when connecting to SQL Server from any database tools from your desktop. For example, when connecting via the Azure Data Studio (mentioned below), you can connect by using
Localhost,1400instead of justLocalhost. Same with mssql-cli, which is a command line SQL tool.
Check Everything
Now that we've done that, we should be good to go. Let's go through and run a few checks.
Check the Docker container (optional)
You can type the following command to check that the Docker container is running.
In my case I get this:
This tells me that I have two docker containers up and running: one called Bart and the other called Homer.
Connect to SQL Server
Here we use the SQL Server command line tool called 'sqlcmd' inside the container to connect to SQL Server.
Enter your password if prompted.
Now that you're inside the container, connect locally with sqlcmd:
This should bring you to the sqlcmd prompt 1>.
Run a Quick Test
Run a quick test to check that SQL Server is up and running. For example, check the SQL Server version by entering this:
This will bring you to a command prompt 2> on the next line. To execute the query, enter:
Result:
If you see a message like this, congratulations — SQL Server is now up and running on your Mac!
If you prefer to use a GUI to manage SQL Server, read on.
Azure Data Studio
Azure Data Studio is a free GUI management tool that you can use to manage SQL Server on your Mac. You can use it to create and manage databases, write queries, backup and restore databases, and more.
Azure Data Studio is available on Windows, Mac and Linux.
Here are some articles/tutorials I've written for Azure Data Studio:
Another Free SQL Server GUI – DBeaver
Another SQL Server GUI tool that you can use on your Mac (and Windows/Linux/Solaris) is DBeaver.
DBeaver is a free, open source database management tool that can be used on most database management systems (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, Sybase, Microsoft Access, Teradata, Firebird, Derby, and more).
I wrote a little introduction to DBeaver, or you can go straight to the DBeaver download page and try it out with your new SQL Server installation.
By: Sadequl Hussain | Updated: 2017-11-21 | Comments (1) | Related: More >Database Administration
Problem
I am a system administrator / DBA using a Windows laptop. I can remotely connectto our Windows servers from my laptop. Some of my colleagues are using non-Windowssystems like Mac or Linux. Sometimes they also need to access these boxes. How canthey connect?
Solution
System administrators or DBAs often need to access Windows servers remotely.This can be for various reasons like:
- Troubleshooting low disk space
- Running Performance Monitor or Profiler
- Monitoring Windows Event Viewer
- Applying service packs
- Creating and troubleshooting scheduled Windows jobs
- Installing software like SQL Server
- Connecting to another instance from a 'jump host'
- Administering Active Directory
- Etc.
Windows ships with a tool called the 'Remote Desktop Client' to helpconnect to another Windows machine. However, there are users who do not use a Windowsworkstation. Particularly with the spread of open source databases, cloud technologiesand the need for accessing Linux servers, a lot of engineers now use an Apple MacBookor Linux distributions like Fedora or Ubuntu.
Some of these engineers and administrators may need to access Windows hosts.It would make their job much simpler if they had tools similar to the RDP client.
In this tip we will talk about a few remote desktop clients available for Macand Linux. We will talk about their ease of use, features, etc. In a future post,we will talk about Mac and Linux-based database client tools.
Disclaimer
Please be careful when accessing production servers remotely. In most cases,organizations have strict security principles about who can access their servers,so readers need to follow those guidelines. Also, you should not run any commands,queries, or configurations from this tutorial on a production server. In the casewhen you are required to access remote servers and run commands, make sure you areconnected to the right server.
Although we list a number of remote clients from various vendors, this is byno means an exhaustive list. Nor do we endorse any of the products or have any affiliationwith their vendors. The observations made here are purely those of the author.
Also, this tip is not about how to install and configure remote desktop clients.Each software installer package will have its own requirements and dependenciesfor different operating systems; it's not possible to address every issuewhere the package may be failing to install or the client failing to connect toa remote server. This is more of an overview of the tools available.
Remote Desktop Clients
Before going into details, let's talk about the features we want in a remotedesktop client. We wanted tools which:
Sql Server Data Tools For Mac Os
- Are free / open source or at least have a community edition available
- Have active development or product support
- Can map local resources like disk drives or folders to the remote machine
- Allow saving remote desktop sessions for easy future connection
- Allow different screen resolutions
- Enables clipboard sharing between local and remote machines
With these features in mind, let's first see what's available forMac users.
Mac Clients
Microsoft Remote Desktop
For Mac users, Microsoft has released the Microsoft Remote Desktop app, downloadablefrom theMac App store. The application features connection saving, easy searching ofsaved connections, connectivity to Azure RemoteApp and remote resources:
Creating a new connection is fairly simple and intuitive:
Standard features like mapping local directories to remote machine, sound andprinter forwarding are also present:
CoRD
Out next option for the Mac platform is CoRD,downloadable from its sourceforge site. CoRD is also easy to use and offers most features found in otherremote desktop tools.
The image below shows a local folder in a Mac system mapped to a remote Windowsmachine.
Royal TSX
Royal TSX is yet another tool available for Mac fromRoyalApplications. The latest version requires at least the Mac OS Yosemite operatingsystem.
What sets RoyalTSX apart is its ability to use plugins for different types ofconnectivity. These plugins are available from Royal Software as well. The remotedesktop client plugin is installed by default. Similarly, other connection typeslike VNC, SSH, HTTP or FTP can be installed with plugins, making it almost a universalconnectivity tool.
Royal TSX allows repetitive command tasks or key sequences to be run automaticallybefore, after or when a connection is made. The images below show this:
Some plugins allow Windows processes, services or events to be accessed remotely.However, this requires the RoyalTSX server component:
As the image below shows, connecting to a Windows server is fairly simple andstandard. The credentials for the connections need to be created first:
The free version of Royal TSX allows up to 10 remote connections. If you arenot managing dozens of Windows servers, the free version can be a good choice.
Linux Clients
Like Mac, there are remote desktop tools available for different flavors of Linux.To use these tools, needless to say, the Linux computer needs to be running in graphicalmode. Here are few of the tools to consider.
KRDC
KRDC or KDE Remote Desktop Client is available for Linux distros running K Desktop,like Fedora. The package is available from KDE repo, so it can be easily installedwith the following command:
KRDC has a simple interface. However, in our opinion, it lacks a basic featureexpected from any RDP client.
How to make a roux for mac n cheese. All roux starts with a white roux—cooking the roux just long enough to eliminate the taste of raw flour. In a small saucepan, melt the butter (or oil) over medium heat. Add the flour, salt and pepper and stir with a rubber spatula, mixing until they're well combined and the mixture looks smooth.
For example, once a connection is created, KRDC can 'remember' theremote server's username and password, provided it's saved in the KDEWallet Manager application.
This obviously means installing another KDE application in your workstation.The default wallet it looks for is called 'kdewallet' and in a vanillainstallation of KDE Wallet, users don't know the password for that wallet,nor can they change it (at least we could not).
This means when connecting from the KRDC tool, users will be prompted for thewallet's password if the 'Remember password (KWallet)' optionwas chosen. Since users would not know the password, they have to bypass this bypressing the 'Cancel' button:
Bypassing the wallet password prompt will result in the tool asking for the remoteuser's password. Not a show-stopper perhaps, but to most regular users thiscan be a time-consuming affair.
Remmina
In our opinion, this is one of the best tools available for debian-based Linuxdistros, and can be downloaded from theRemmina GitHubrepo of FreeRDP. Unfortunately the installation page does not list any RedHat-baseddistros except Fedora. If you are using something like Ubuntu, Gentoo, Fedora orArchLinux, this tool should be yours.
The two images below show a remote Windows desktop displayed in Remmina runningin Ubuntu 16.10:
Other than RDP, this tool also supports NX, VNC and SSH protocols:
Some of the advanced features of Remmina connection properties are shown below:
Like RoyalTSX for Mac, this tool also allows for startup programs to run whena connection is made.
FreeRDP

Another tool from the same repo owner is FreeRDP, a command line tool to startremote desktop sessions. This is available from theGitHubpage of the product. FreeRDP is available for Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and OpenSuSEin Linux distributions and for Mac and even Windows. As said, this is a commandline tool, but has a large number of options available as switches.
We installed the tool in a Fedora 26 machine and were able to connect to a WindowsServer. The actual command is xfreerdp and it's located in the /usr/bin directory.The following code snippet shows a basic form of the command and its output. Inthis case, we can safely ignore the warning:
Other Remote Desktop Sharing Protocols
So far, the tools we have talked about all use the remote desktop protocol. Thisis a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft and ships with any Windows machine.It runs on port 3389 by default. However, this is not the only protocol availablefor remote connections. We will talk about two other protocols:
- VNC
- NX
VNC
VNC or Virtual Network Computing is a desktop sharing system using the RemoteFrame Buffer (RFB) protocol. Computers running a VNC server can be remotely connectedfrom other computers running a VNC client. This is a platform independent protocol,which means there are servers and clients available for Mac, Linux and Windows.This also means the same VNC client can connect to a remote Windows server or aLinux server, each of which could be running VNC as a service. In fact someof the RDP tools we have discussed so far like Remmina, KRDC or RoyalTSX - all featurea VNC client. The default port for VNC communication is 5900. For Java-based VNCclient, this is 5800.
Although VNC can be an alternative to remote desktop protocol, it means installationof additional software on the Windows server and configuring any firewall to allowtraffic on the VNC port.
How is norma?. There are various VNC client and server packages available for free, some ofthese are:
- TightVNC
- TigerVNC
- RealVNC Home Edition
- UltraVNC
The image below shows the UltraVNC service running in a Windows Server 2016 machine.We downloaded it from UltraVNC'sofficial site.
And here are some of the UltraVNC service configurations:
The image below shows how we are using a TigerVNC Viewer client from a CentOS7.16 machine to connect to the Windows server running UltraVNC.
Sql Server Data Tools For Mac
NX
NX is another remote desktop sharing protocol developed by a company called NoMachine(there are also open source variants like OpenNX and FreeNX). The tool, also calledNoMachine, allows some cool features like recording the remote desktop sessionsor streaming remote multimedia. Unlike VNC or RDP, NoMachine does not have separatesoftware installers for client and server: a NoMachine install creates both thecomponents. Once NoMachine is installed in a Windows server, make sure the serviceis running and the firewall is allowing traffic through the default port of 4000.
In the image below, we can see the nxservice (NoMachine server) running as aWindows service:
The following series of images show a NoMachine client running in Fedora settingup a remote Windows server connection:
Once the connection is set up, subsequent connections are easy: just select theconnection icon and click on the 'Connect' button:
Once the credentials are provided (here we are using password authentication),there are a number of options to choose from for logon, display, resolution, sound,multimedia, etc.:
As you can see, NoMachine provides lot of options to configure how you interactwith the remote computer. Once you click through the options, the remote desktopis shown as a locked screen:
You can now press Ctl+Alt+0 to bring out the NoMachine menu, click on the littleicon in the lower right corner and choose Ctl+Alt+Delete from the pop-up menu, thenclick on the 'Done' button:
This will bring up the Windows logon screen where you can put the remote server'saccess credentials.
Conclusion
One thing to remember when troubleshooting remote desktop session issues is thenetworking layer. For any remote desktop connection to succeed:
- The service component needs to be running in the remote machine, whetherit is remote desktop service, VNC or NX.
- The remote server needs to have a network path from the client: for example,we cannot remote desktop into a server if it's only accessible from abastion host.
- The server's firewall or other network protection layer has to allowremote desktop traffic coming from the client's network. This is particularlytrue if the machine is running VNC or NX.
- When running the Windows remote desktop protocol and client, the user needsto be a member of the remote desktop users local Windows group other groupswith higher privileges.
- The network bandwidth needs to be good, particularly if there is a largegeographical distance between client and server.
We hope this tip has given you some ideas about choosing the right RDP tool.We leave it up to the reader to make their own choice. Feel free to comment aboutother non-Windows RDP clients you might be using in the comments section below.
Sql Server Command Line Tools For Mac
Next Steps
If you are using a non-Windows workstation, consider the following:
Sql Server Tools For Mac
- Download and install the RDP clients we talked about
- Test the limitations of the 'free' editions; for example:
- How many remote sessions you can keep open or
- How many sessions you can save
Last Updated: 2017-11-21

Docker is a platform that enables software to run in its own isolated environment. Therefore, SQL Server 2019 can be run on Docker in its own isolated container.
Install Docker
To download, visit the Docker CE for Mac download page and click Get Docker.
To install, double-click on the .dmg file and then drag the Docker.app icon to your Application folder.
Launch Docker
Launch Docker the same way you'd launch any other application (eg, via the Applications folder, the Launchpad, etc).
When you open Docker, you might be prompted for your password so that Docker can install its networking components and links to the Docker apps. Go ahead and provide your password, as Docker needs this to run.
Increase the Memory (optional)
By default, Docker will have 2GB of memory allocated to it. I'd suggest increasing it to 4GB if you can.
To do this, select Preferences from the little Docker icon in the top menu:
Then finish off by clicking Apply & Restart
SQL Server
Now that Docker has been installed and configured, we can download and install SQL Server 2019.
Download SQL Server 2019
Open a Terminal window and run the following command.
This downloads the latest SQL Server for Linux Docker image to your computer.
You can also check for the various container image options on the Docker website if you wish.
Launch the Docker Image
Run the following command to launch an instance of the Docker image you just downloaded:
Just change
Bartto a name of your choosing, andreallyStrongPwd#123to a password of your choosing.If you get a 'port already allocated' error, see below.
Here's an explanation of the parameters:
-e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y'- The
Yshows that you agree with the EULA (End User Licence Agreement). This is required. -e 'SA_PASSWORD=reallyStrongPwd#123'- Required parameter that sets the
sadatabase password. -p 1433:1433- This maps the local port 1433 to port 1433 on the container. The first value is the TCP port on the host environment. The second value is the TCP port in the container.
--name Bart- Another optional parameter. This parameter allows you to name the container. This can be handy when stopping and starting your container from the Terminal. You might prefer to give it a more descriptive name like
sql_server_2019or similar. -d- This optional parameter launches the Docker container in daemon mode. This means that it runs in the background and doesn't need its own Terminal window open. You can omit this parameter to have the container run in its own Terminal window.
mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2019-latest- This tells Docker which image to use.
Password Strength
You need to use a strong password. Microsoft says this about the password:
The password should follow the SQL Server default password policy, otherwise the container can not setup SQL server and will stop working. By default, the password must be at least 8 characters long and contain characters from three of the following four sets: Uppercase letters, Lowercase letters, Base 10 digits, and Symbols.
Error – 'Port already allocated'?
If you get an error that says something about 'port is already allocated', then perhaps you already have SQL Server installed on another container that uses that port. In this case, you'll need to map to a different port on the host.
Therefore, you could change the above command to something like this:
In this case I simply changed
-p 1433:1433to-p 1400:1433. Everything else remains the same.You may now get an error saying that you need to remove the existing container first. To do that, run the following (but swap
Bartwith the name of your own container):Once removed, you can try running the previous command again.
Note that if you change the port like I've done here, you will probably need to include the port number when connecting to SQL Server from any database tools from your desktop. For example, when connecting via the Azure Data Studio (mentioned below), you can connect by using
Localhost,1400instead of justLocalhost. Same with mssql-cli, which is a command line SQL tool.
Check Everything
Now that we've done that, we should be good to go. Let's go through and run a few checks.
Check the Docker container (optional)
You can type the following command to check that the Docker container is running.
In my case I get this:
This tells me that I have two docker containers up and running: one called Bart and the other called Homer.
Connect to SQL Server
Here we use the SQL Server command line tool called 'sqlcmd' inside the container to connect to SQL Server.
Enter your password if prompted.
Now that you're inside the container, connect locally with sqlcmd:
This should bring you to the sqlcmd prompt 1>.
Run a Quick Test
Run a quick test to check that SQL Server is up and running. For example, check the SQL Server version by entering this:
This will bring you to a command prompt 2> on the next line. To execute the query, enter:
Result:
If you see a message like this, congratulations — SQL Server is now up and running on your Mac!
If you prefer to use a GUI to manage SQL Server, read on.
Azure Data Studio
Azure Data Studio is a free GUI management tool that you can use to manage SQL Server on your Mac. You can use it to create and manage databases, write queries, backup and restore databases, and more.
Azure Data Studio is available on Windows, Mac and Linux.
Here are some articles/tutorials I've written for Azure Data Studio:
Another Free SQL Server GUI – DBeaver
Another SQL Server GUI tool that you can use on your Mac (and Windows/Linux/Solaris) is DBeaver.
DBeaver is a free, open source database management tool that can be used on most database management systems (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQLite, Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, Sybase, Microsoft Access, Teradata, Firebird, Derby, and more).
I wrote a little introduction to DBeaver, or you can go straight to the DBeaver download page and try it out with your new SQL Server installation.
By: Sadequl Hussain | Updated: 2017-11-21 | Comments (1) | Related: More >Database Administration
Problem
I am a system administrator / DBA using a Windows laptop. I can remotely connectto our Windows servers from my laptop. Some of my colleagues are using non-Windowssystems like Mac or Linux. Sometimes they also need to access these boxes. How canthey connect?
Solution
System administrators or DBAs often need to access Windows servers remotely.This can be for various reasons like:
- Troubleshooting low disk space
- Running Performance Monitor or Profiler
- Monitoring Windows Event Viewer
- Applying service packs
- Creating and troubleshooting scheduled Windows jobs
- Installing software like SQL Server
- Connecting to another instance from a 'jump host'
- Administering Active Directory
- Etc.
Windows ships with a tool called the 'Remote Desktop Client' to helpconnect to another Windows machine. However, there are users who do not use a Windowsworkstation. Particularly with the spread of open source databases, cloud technologiesand the need for accessing Linux servers, a lot of engineers now use an Apple MacBookor Linux distributions like Fedora or Ubuntu.
Some of these engineers and administrators may need to access Windows hosts.It would make their job much simpler if they had tools similar to the RDP client.
In this tip we will talk about a few remote desktop clients available for Macand Linux. We will talk about their ease of use, features, etc. In a future post,we will talk about Mac and Linux-based database client tools.
Disclaimer
Please be careful when accessing production servers remotely. In most cases,organizations have strict security principles about who can access their servers,so readers need to follow those guidelines. Also, you should not run any commands,queries, or configurations from this tutorial on a production server. In the casewhen you are required to access remote servers and run commands, make sure you areconnected to the right server.
Although we list a number of remote clients from various vendors, this is byno means an exhaustive list. Nor do we endorse any of the products or have any affiliationwith their vendors. The observations made here are purely those of the author.
Also, this tip is not about how to install and configure remote desktop clients.Each software installer package will have its own requirements and dependenciesfor different operating systems; it's not possible to address every issuewhere the package may be failing to install or the client failing to connect toa remote server. This is more of an overview of the tools available.
Remote Desktop Clients
Before going into details, let's talk about the features we want in a remotedesktop client. We wanted tools which:
Sql Server Data Tools For Mac Os
- Are free / open source or at least have a community edition available
- Have active development or product support
- Can map local resources like disk drives or folders to the remote machine
- Allow saving remote desktop sessions for easy future connection
- Allow different screen resolutions
- Enables clipboard sharing between local and remote machines
With these features in mind, let's first see what's available forMac users.
Mac Clients
Microsoft Remote Desktop
For Mac users, Microsoft has released the Microsoft Remote Desktop app, downloadablefrom theMac App store. The application features connection saving, easy searching ofsaved connections, connectivity to Azure RemoteApp and remote resources:
Creating a new connection is fairly simple and intuitive:
Standard features like mapping local directories to remote machine, sound andprinter forwarding are also present:
CoRD
Out next option for the Mac platform is CoRD,downloadable from its sourceforge site. CoRD is also easy to use and offers most features found in otherremote desktop tools.
The image below shows a local folder in a Mac system mapped to a remote Windowsmachine.
Royal TSX
Royal TSX is yet another tool available for Mac fromRoyalApplications. The latest version requires at least the Mac OS Yosemite operatingsystem.
What sets RoyalTSX apart is its ability to use plugins for different types ofconnectivity. These plugins are available from Royal Software as well. The remotedesktop client plugin is installed by default. Similarly, other connection typeslike VNC, SSH, HTTP or FTP can be installed with plugins, making it almost a universalconnectivity tool.
Royal TSX allows repetitive command tasks or key sequences to be run automaticallybefore, after or when a connection is made. The images below show this:
Some plugins allow Windows processes, services or events to be accessed remotely.However, this requires the RoyalTSX server component:
As the image below shows, connecting to a Windows server is fairly simple andstandard. The credentials for the connections need to be created first:
The free version of Royal TSX allows up to 10 remote connections. If you arenot managing dozens of Windows servers, the free version can be a good choice.
Linux Clients
Like Mac, there are remote desktop tools available for different flavors of Linux.To use these tools, needless to say, the Linux computer needs to be running in graphicalmode. Here are few of the tools to consider.
KRDC
KRDC or KDE Remote Desktop Client is available for Linux distros running K Desktop,like Fedora. The package is available from KDE repo, so it can be easily installedwith the following command:
KRDC has a simple interface. However, in our opinion, it lacks a basic featureexpected from any RDP client.
How to make a roux for mac n cheese. All roux starts with a white roux—cooking the roux just long enough to eliminate the taste of raw flour. In a small saucepan, melt the butter (or oil) over medium heat. Add the flour, salt and pepper and stir with a rubber spatula, mixing until they're well combined and the mixture looks smooth.
For example, once a connection is created, KRDC can 'remember' theremote server's username and password, provided it's saved in the KDEWallet Manager application.
This obviously means installing another KDE application in your workstation.The default wallet it looks for is called 'kdewallet' and in a vanillainstallation of KDE Wallet, users don't know the password for that wallet,nor can they change it (at least we could not).
This means when connecting from the KRDC tool, users will be prompted for thewallet's password if the 'Remember password (KWallet)' optionwas chosen. Since users would not know the password, they have to bypass this bypressing the 'Cancel' button:
Bypassing the wallet password prompt will result in the tool asking for the remoteuser's password. Not a show-stopper perhaps, but to most regular users thiscan be a time-consuming affair.
Remmina
In our opinion, this is one of the best tools available for debian-based Linuxdistros, and can be downloaded from theRemmina GitHubrepo of FreeRDP. Unfortunately the installation page does not list any RedHat-baseddistros except Fedora. If you are using something like Ubuntu, Gentoo, Fedora orArchLinux, this tool should be yours.
The two images below show a remote Windows desktop displayed in Remmina runningin Ubuntu 16.10:
Other than RDP, this tool also supports NX, VNC and SSH protocols:
Some of the advanced features of Remmina connection properties are shown below:
Like RoyalTSX for Mac, this tool also allows for startup programs to run whena connection is made.
FreeRDP
Another tool from the same repo owner is FreeRDP, a command line tool to startremote desktop sessions. This is available from theGitHubpage of the product. FreeRDP is available for Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and OpenSuSEin Linux distributions and for Mac and even Windows. As said, this is a commandline tool, but has a large number of options available as switches.
We installed the tool in a Fedora 26 machine and were able to connect to a WindowsServer. The actual command is xfreerdp and it's located in the /usr/bin directory.The following code snippet shows a basic form of the command and its output. Inthis case, we can safely ignore the warning:
Other Remote Desktop Sharing Protocols
So far, the tools we have talked about all use the remote desktop protocol. Thisis a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft and ships with any Windows machine.It runs on port 3389 by default. However, this is not the only protocol availablefor remote connections. We will talk about two other protocols:
- VNC
- NX
VNC
VNC or Virtual Network Computing is a desktop sharing system using the RemoteFrame Buffer (RFB) protocol. Computers running a VNC server can be remotely connectedfrom other computers running a VNC client. This is a platform independent protocol,which means there are servers and clients available for Mac, Linux and Windows.This also means the same VNC client can connect to a remote Windows server or aLinux server, each of which could be running VNC as a service. In fact someof the RDP tools we have discussed so far like Remmina, KRDC or RoyalTSX - all featurea VNC client. The default port for VNC communication is 5900. For Java-based VNCclient, this is 5800.
Although VNC can be an alternative to remote desktop protocol, it means installationof additional software on the Windows server and configuring any firewall to allowtraffic on the VNC port.
How is norma?. There are various VNC client and server packages available for free, some ofthese are:
- TightVNC
- TigerVNC
- RealVNC Home Edition
- UltraVNC
The image below shows the UltraVNC service running in a Windows Server 2016 machine.We downloaded it from UltraVNC'sofficial site.
And here are some of the UltraVNC service configurations:
The image below shows how we are using a TigerVNC Viewer client from a CentOS7.16 machine to connect to the Windows server running UltraVNC.
Sql Server Data Tools For Mac
NX
NX is another remote desktop sharing protocol developed by a company called NoMachine(there are also open source variants like OpenNX and FreeNX). The tool, also calledNoMachine, allows some cool features like recording the remote desktop sessionsor streaming remote multimedia. Unlike VNC or RDP, NoMachine does not have separatesoftware installers for client and server: a NoMachine install creates both thecomponents. Once NoMachine is installed in a Windows server, make sure the serviceis running and the firewall is allowing traffic through the default port of 4000.
In the image below, we can see the nxservice (NoMachine server) running as aWindows service:
The following series of images show a NoMachine client running in Fedora settingup a remote Windows server connection:
Once the connection is set up, subsequent connections are easy: just select theconnection icon and click on the 'Connect' button:
Once the credentials are provided (here we are using password authentication),there are a number of options to choose from for logon, display, resolution, sound,multimedia, etc.:
As you can see, NoMachine provides lot of options to configure how you interactwith the remote computer. Once you click through the options, the remote desktopis shown as a locked screen:
You can now press Ctl+Alt+0 to bring out the NoMachine menu, click on the littleicon in the lower right corner and choose Ctl+Alt+Delete from the pop-up menu, thenclick on the 'Done' button:
This will bring up the Windows logon screen where you can put the remote server'saccess credentials.
Conclusion
One thing to remember when troubleshooting remote desktop session issues is thenetworking layer. For any remote desktop connection to succeed:
- The service component needs to be running in the remote machine, whetherit is remote desktop service, VNC or NX.
- The remote server needs to have a network path from the client: for example,we cannot remote desktop into a server if it's only accessible from abastion host.
- The server's firewall or other network protection layer has to allowremote desktop traffic coming from the client's network. This is particularlytrue if the machine is running VNC or NX.
- When running the Windows remote desktop protocol and client, the user needsto be a member of the remote desktop users local Windows group other groupswith higher privileges.
- The network bandwidth needs to be good, particularly if there is a largegeographical distance between client and server.
We hope this tip has given you some ideas about choosing the right RDP tool.We leave it up to the reader to make their own choice. Feel free to comment aboutother non-Windows RDP clients you might be using in the comments section below.
Sql Server Command Line Tools For Mac
Next Steps
If you are using a non-Windows workstation, consider the following:
Sql Server Tools For Mac
- Download and install the RDP clients we talked about
- Test the limitations of the 'free' editions; for example:
- How many remote sessions you can keep open or
- How many sessions you can save
Last Updated: 2017-11-21
About the author
Sql Server Query Tool For Mac
View all my tips

